CS 61B Berkeley - Java and Data Structures Review
My review for CS 61B Berkeley
The most common way to execute a Java program is to run it through a sequence of two programs. The first is the Java compiler, or javac. The second is the Java interpreter, or java.

javac HelloWorld.java
java HelloWorldpublic class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world!");
}
}Variables in Java are strictly defined with a specific type. You can’t change the type of variable after defining it.
System.out.printlnprints to screen (like stdout), with\nat the end of lineSystem.out.printsame as above but without\n
Conditional statements are similar to JavaScript.
Data Types
Primitive Types
There are 8 primitive types in Java:
byteshortintlongfloatdouble— stores approximations of real numbersbooleanchar
Reference Type
- References to Objects
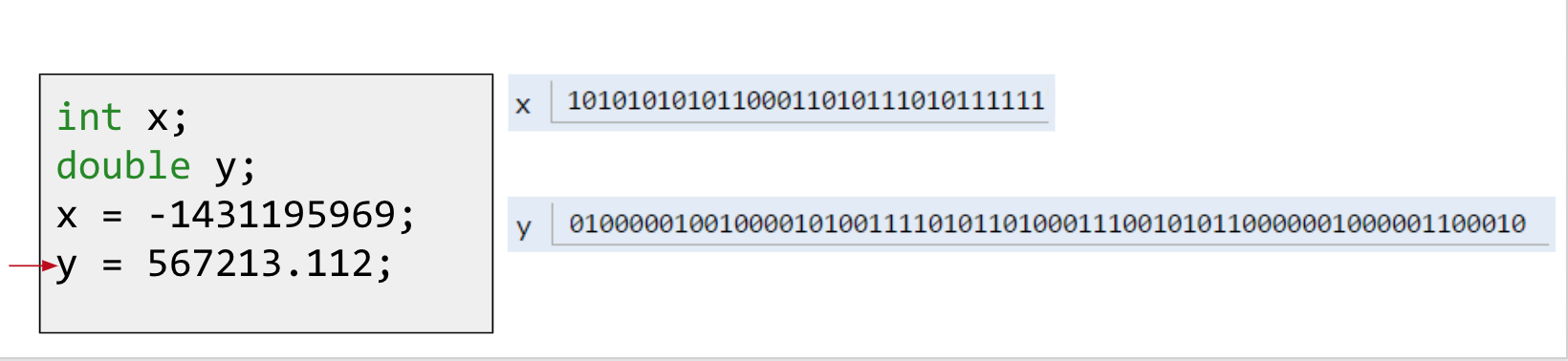
When you declare a variable of a certain type in Java:
- Your computer sets aside exactly enough bits to hold a thing of that type. Example: Declaring an
intsets aside a “box” of 32 bits. - Java creates an internal table that maps each variable name to a location.
- Java does NOT write anything into the reserved boxes — for safety, Java will not let you access a variable that is uninitialized.
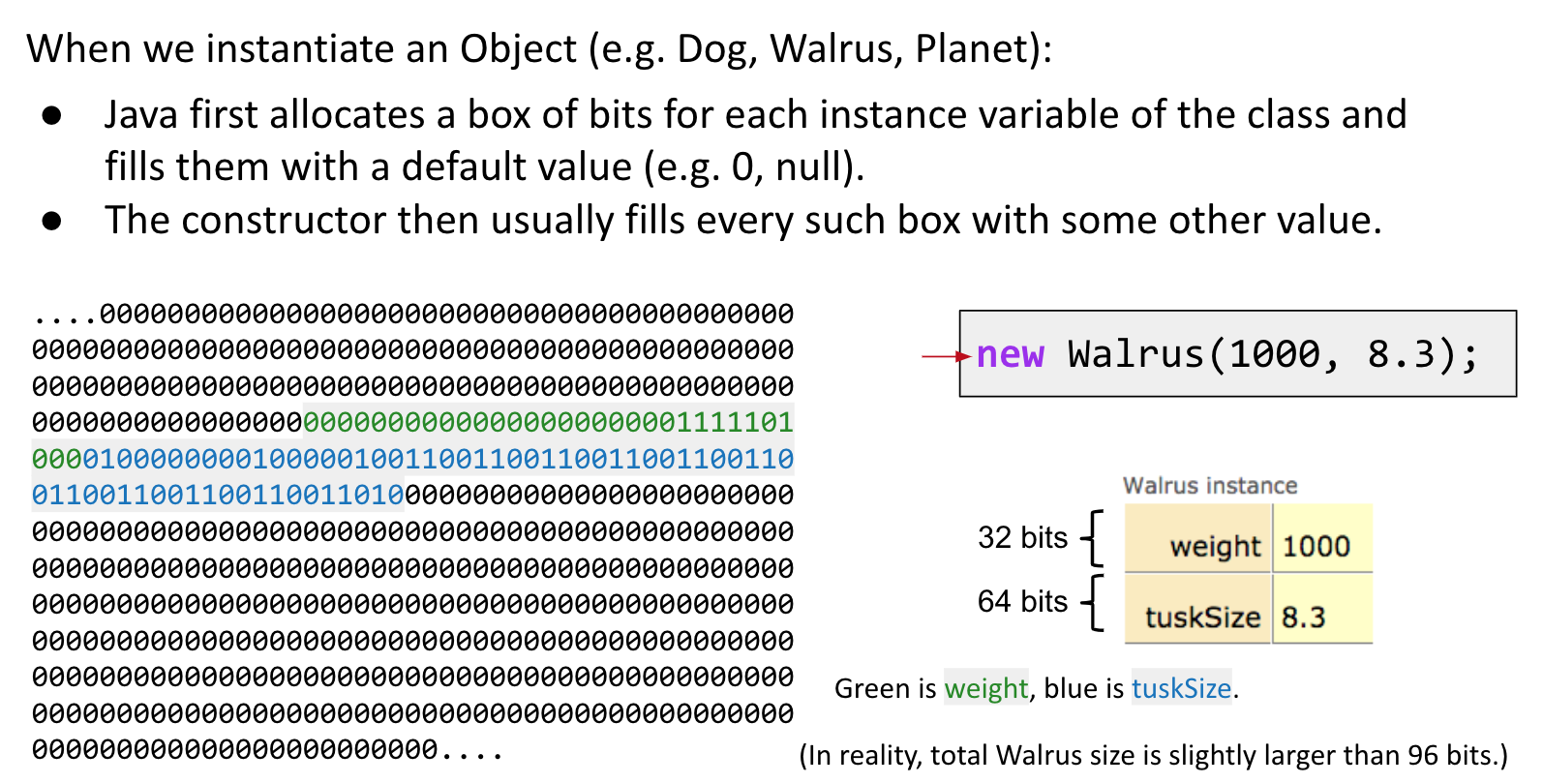
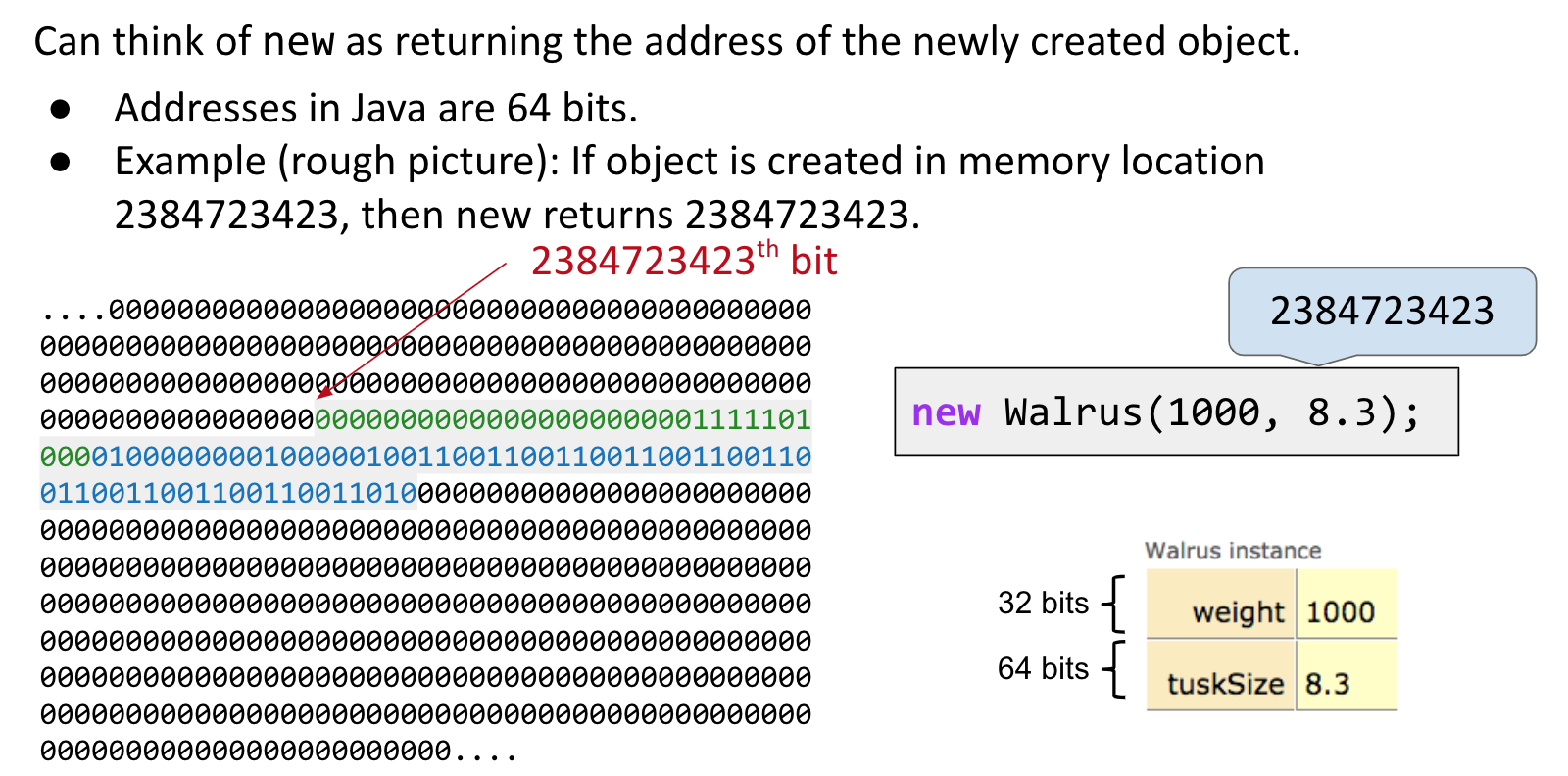
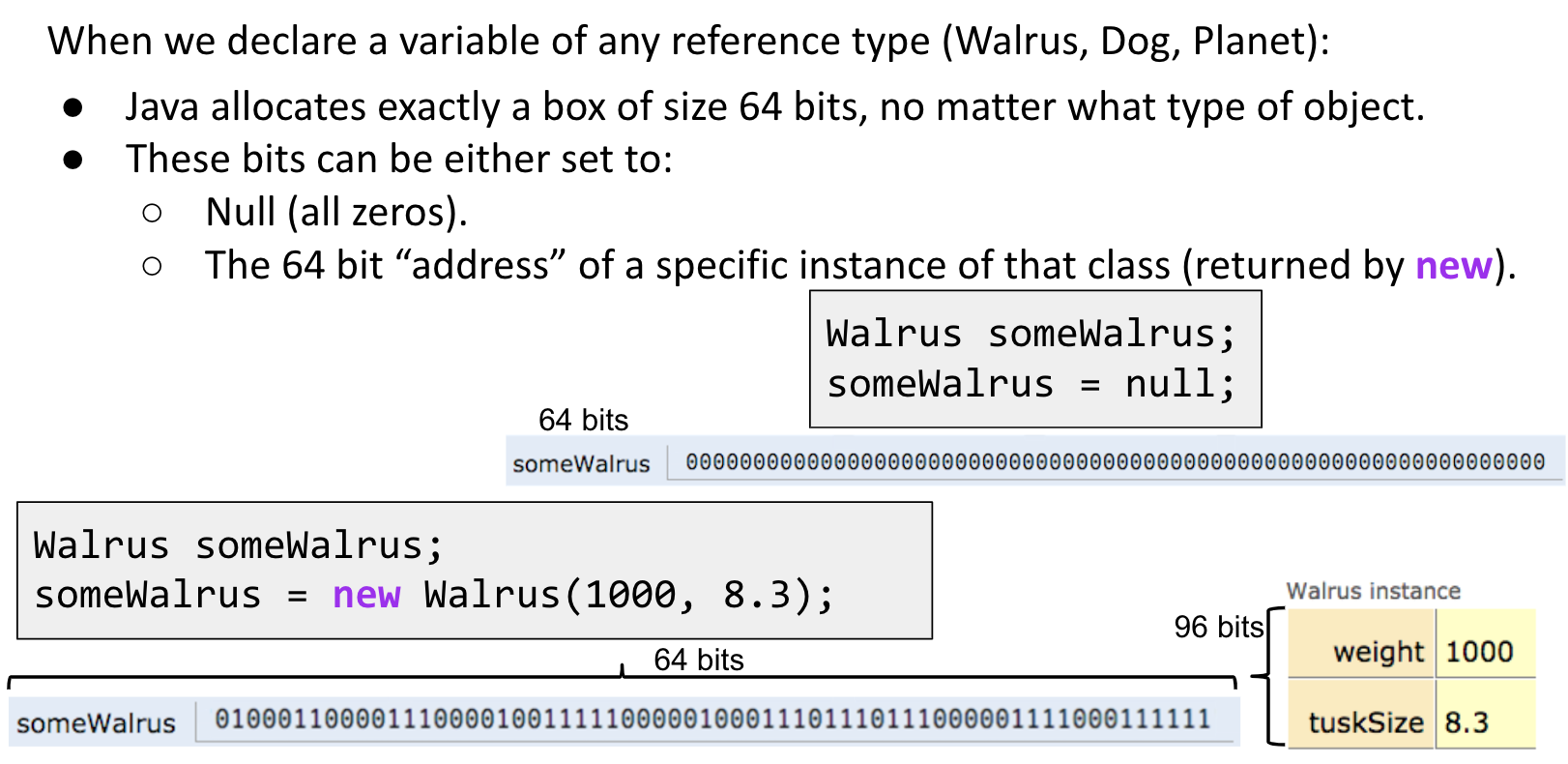
The Golden Rule of Equals (GRoE)
Given variables y and x:
y = x copies all the bits from x into y.


Use the private keyword to prevent code in other classes from using members (or constructors) of a class.
Functions
public static int max(int x, int y) {
if (x > y) {
return x;
}
return y;
}Same as in C, we declare functions with name, type of output, and parameters.
Arrays
int[] numbers = new int[3];
numbers[0] = 4;
numbers[1] = 7;
numbers[2] = 10;
// Or this way
int[] numbers = new int[]{4, 7, 10};We create a new instance of class int named numbers which is an array of 3 integers. You can get the length of an array by using .length.
For Loop
for loop syntax is similar to JavaScript. break and continue work similarly as well:
continue— skips the rest of the current iteration and jumps to the next increment conditionbreak— terminates the innermost loop
Enhanced For Loop
String[] arr = {"x", "y"};
for (String element : arr) {
System.out.println(element);
}This is similar to for in in Python.
Object-Oriented Programming
// This class can be run directly because it has main() method
// Similar idea as C
public class Otoke {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
// This class can't be run directly because there is no main method
class Dog {
// weight is an Instance variable
public int weight;
// Static method or variable can only be accessed by Class, not instance
public static String TYPE = "animal";
// Constructor: (similar to a method, but not a method)
// Determines how to instantiate the class
public Dog(int initWeight) {
weight = initWeight;
}
// Non-static method, a.k.a. Instance Method
// If the method needs to use "instance variables",
// the method must be non-static
public void doubleWeight() {
System.out.println(weight * 2);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog smallDog; // Declaration of a Dog variable
new Dog(20); // Instantiation of the Dog class
smallDog = new Dog(5); // Instantiation and Assignment
Dog hugeDog = new Dog(150); // Declaration, Instantiation and Assignment
}
}- Static methods are invoked using the class name:
Dog.makeNoise(); - Instance methods are invoked using an instance name:
maya.makeNoise(); - Static methods can’t access instance variables, because there is no “me”
Command Line Arguments
public static void main(String[] args)
// args is an array of command line arguments
// access item in array by args[index]
// args[0] means first argument after filenameNested Classes
public class SLList {
public class IntNode { // Define a class inside another
public int item;
}
private IntNode stuff; // Use that to declare a new variable
}Nested Classes are useful when a class doesn’t stand on its own and is obviously subordinate to another class.
- Make the nested class private if other classes should never use the nested class
- Declare it static if the nested class never uses any instance variables or methods of the outer class
- Static classes cannot access outer class’s instance variables or methods
- Results in a minor savings of memory

Caching
Caching idea: putting aside data to speed up retrieval.
Every time we add a new node to SLList, we increment the size variable (which is an instance variable). When removing a node, we decrement it.
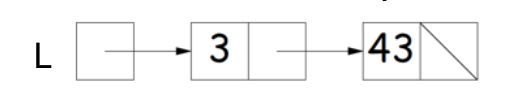
SLList - Singly Linked List
Suppose we have a naked linked list (simply a node):
public class IntNode {
public int item; // Item is the integer part of each node
public IntNode next; // next is a "pointer"/reference to the next IntNode
public IntNode(int i, IntNode n) { // Initiation of the node
item = i;
next = n;
}
}
For better handling with lists, we can wrap the node above inside a Singly Linked List:
public class SLList {
private static class IntNode {
private int item;
private IntNode next;
private IntNode(int i, IntNode n) {
item = i;
next = n;
}
}
}